Going to SXSW Interactive?
Stop in at Jane McGonigal's talk about SuperBetter.com and you might see some of what I've been working on lately.
What I Did Last Weekend (for One Hour): Prototyping
The interactive demo. This allows users to see what appliances are using how much energy during the course of a day (in this example; users could specify the time/date range of the slider). This was a quick proto build in Axure RP, and is really rough, but gets the proof-of-concept across.
What I Did Last Weekend (for One Hour): Wireframing
This is the result of a one-hour wireframing exercise for a job interview. The brief was to create a home page/dashboard that had visualizations of home energy use and how to reduce it. More tools and visualizations are in the links.
Two Things You Want to Hear from Customer Service
Whether it's tech support for your computer, or HVAC, or a government agency, or your health insurance company: 1. Click click click. "Oh, I see what's going on."
2. "There, that should take care of it."
The first means that the company gives customer-facing personnel direct access to account info and the entire flow of decisions affecting it.
The second means that customer-facing personnel can actually make decisions and reach into the spaghetti of rules, regulations, and settings to fix something.
(My small ISP is a good example of both; Blue Shield is a bad example of both.)
In Which I Kind of Defend the IRS
Talking Points Memo is reporting (with a very clear chart) on the scale of the "tax gap". This gap, which unlike a "missile gap" or "shoe gap" other blind calls to blind action, seems to be real, and is defined as the delta between taxes owed and taxes paid in a fiscal year. As TPM's chart, based on numbers from the nonpartisan Center on Budget and Policy Priorities, shows, the 2006 tax gap was $385 billion-with-a-b. This is second only to the $521 billion of military expenditures, larger than the $330 billion of Medicare spending, and a good sight more than the as-of-2006 $248 billion deficit. Neither TPM nor the CBPP go into detailed breakdowns of the gap's composition, but the CBPP was able to pick out the plurality culprit: underreporting of income. "Sole proprietors, a major class of small businesses, report less than half of their income to the IRS. In fact, under-reported business income is the single largest source of the tax gap, amounting to fully $122 billion in 2006 alone."
(This is not to pick on small businesses, the mythical all-American engine of the U.S. economy -- for dissent on that common assumption, see this NPR report. And this is not to let off the hook the "1-percenters" who move what would normally be "income" to "investment" by taking pay in stock options or other means, or place their money off-shore, or use any number of complicated dodges to end up paying low, if non-zero, tax bills. It's just that there are relatively many small business versus relatively few "fat cats", so in this case quantity of tax dodging overwhelms quality.)
It seems like a no-brainer, especially for those who spent this last summer forcing a Constitutional crisis over their avowed concern over the Federal deficit. (Or debt. They aren't always good at keeping the two straight.) These are bills that are due, bills defined and determined by tax laws agreed upon by Congress and state legislatures -- the very people who threatened a shutdown of the government over deficit issues, the very people who want to gut social programs, or kill Federal contributions to Planned Parenthood, or zero out foreign aid, as though the aggregate of those would be even a tenth of $385 billion. (Hint: they aren't. Not even close.)
A key finding in the CBPP report is this: "In the areas of the tax code with substantial information reporting and withholding requirements — most notably workers’ wages, which employers report to the IRS and on which they withhold income and payroll taxes — compliance is extremely high."
Let's go over that again. Where there are strong regulations on reporting, with enforcement, there's no problem. People report and pay their fair share, and are in the game the way it was designed, allowing other people to play fairly also. In contrast, the CBPP reports, "where there is no third-party information reporting or withholding, tax collections are abysmal."
Of course, knowing tax law, and what to report for income, can be a difficult task. No doubt reform could help some of those honestly baffled people. (Personal note: I long ago realized that paying someone to do my taxes saved me more than the equivalent in my hourly wage times the hours it'd take to understand what the hell some of these forms mean). There is generations-upon-generations of tax code, which has endured alteration and appending and what-have-you. Programmers, think of the code of a legacy application that's been worked on by hundreds of people over a decade -- spaghetti code. But the evidence shows that where there is strong regulation, there is strong compliance.
Now, how did we get here?
Just looking at the CBPP report, one can see that filling those tax code holes with strong reporting regulations would help. To quote at length:
"The Bush Administration pushed successfully for new withholding requirements on government contractors on the heels of troubling Government Accountability Office investigations showing widespread tax abuse. Then, in the 2010 health reform law, the Obama Administration teamed up with congressional Democrats to tighten reporting requirements on certain business transactions. These were two modest but real steps forward.
The current Congress, however, repealed both measures. To make matters worse, in last year’s deficit-reduction legislation (the Budget Control Act), House Republicans blocked Senate Majority Leader Reid’s effort to ensure sufficient funding for IRS tax compliance activities, even though the Congressional Budget Office concluded that it would have generated net budget savings of $30 billion over a decade."
So the first problem is resistance to clarifying and placing strong tax code. Debate amongst yourselves where the blame falls.
A second reason is that over the last decade, various administrations and political/private forces have pressed to cut support for the IRS. This is similar to how gutting the budgets of environmental and financial regulation departments at the Federal level have left giant holes for bad behavior at minimal cost. Recently, for example, we've seen the SEC have to settle slam-dunk cases, such as against Goldman Sachs, for relatively paltry sums, with no future leverage such as legal precedent, criminal convictions, and so on -- simply because the government agency in question does not have the resources to pursue prosecution or even audit for compliance.
You can see a teacup version of this in the 2006 move by the Bush administration to fire nearly half the IRS lawyers who audited tax returns on "some of the wealthiest Americans, specifically those who are subject to gift and estate taxes when they transfer parts of their fortunes to their children and others." That administration pushed hard to alter legislation to kill the estate ("death") tax, couldn't pull it off, so went after those who enforced it, or even just checked for it. Can't figure out how to rob a bank? Maybe if you could get the security staff laid off, it'd be easier.
This is still going on. Just recently the IRS reported that it's increasingly unable to do its job due to budget cuts and staffing. From the article: "Mr. Obama last year asked for the I.R.S. budget of $12.1 billion to be increased by more than $1 billion, to enable it to hire 5,100 employees. But Republicans, who oppose the health care program, succeeded in trimming the agency’s funds to $11.8 billion in the budget approved last month."
Of course, nobody likes audits, the idea of them or the practice. It is a painful process. But three things.
First: This is how we do. Though we may disagree with how the tax revenue is spent -- and that's healthy, on both sides of the political spectrum -- it is the cost of living in a civilization. And it's important to realize that tax cheating disproportionally benefits the top of the wealth scale, while taking away from those near or on the bottom. Though this could be seen as all the more incentive for the $50k/year small businessman, or waitron, to shave a little off the income reporting, my point is that we would all be better off with more consistent enforcement.
Second: These cuts don't just mean fewer audits. The affected IRS staff are also your Help Desk. Part of the reason audits are such a painful process is because we, as individual tax filers, might not have been sure of something, and had to make a good-faith effort. And we might have been wrong to some degree. But the cuts to the IRS staff don't just mean fewer evil auditors, but fewer people to answer our questions on April 14. This cuts our ability to figure out what the hell is going on in Line 48a: "Those demands have strained the I.R.S.’s ability to respond to inquiries from the public. Nearly half the taxpayers who wrote or faxed questions waited more than six weeks for a response, the report found. Taxpayers who telephoned for information found backlogs, too, the report said, as three in 10 calls went unanswered."
Third: You know, it doesn't cost that much, as a proportion of the Federal budget, to hire back these staffers. Certainly only a few million, tops. Even if they could reduce five percent of the tax gap, that'd be over $19 billion, based on 2006 numbers. That's a pretty good cost-benefit ratio, yes?
Fully funding Head Start is less than $8 billion a year. Worth it?
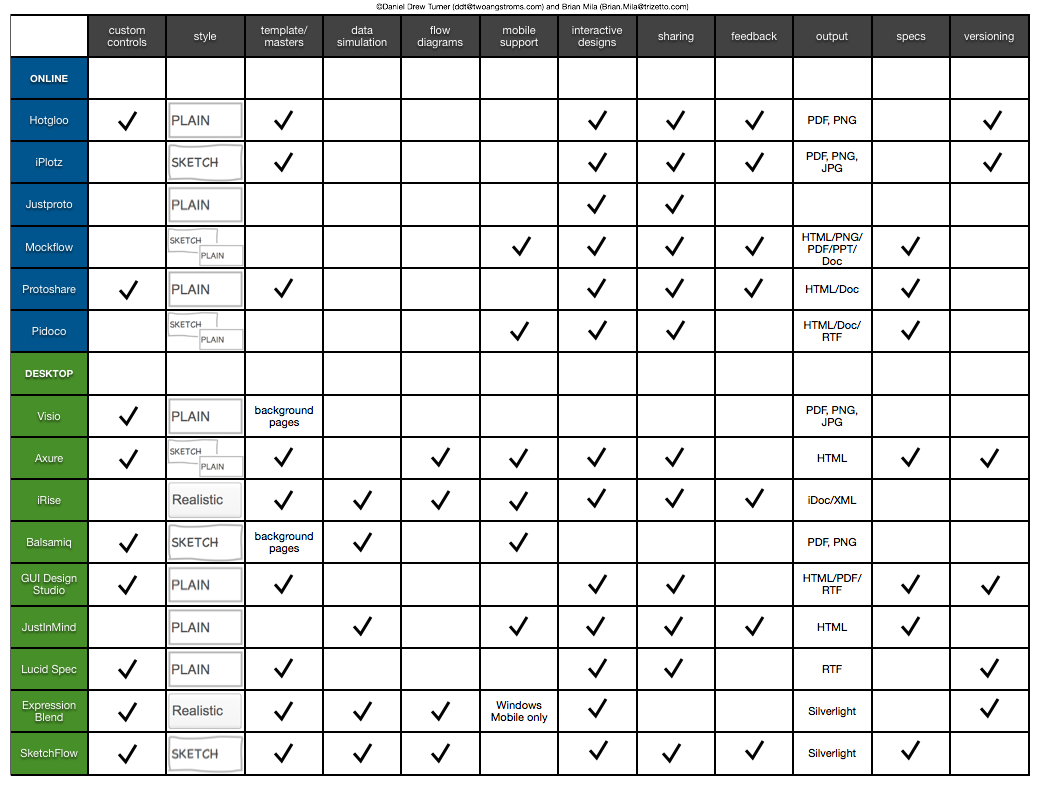
UX Prototyping/Wireframing Tool Comparo
These graphics are built off of the data compiled by Brian Mila, Senior Product Designer at The TriZetto Group. Current as of early January 2012.
A comparison of annual license costs for the UX tools
Hitler at the St. Brigid St. Book Club
Timothy W. Ryback's "Hitler's Private Library: The Books That Shaped His Life" recounts how the author pored through 1,200 out of an estimated 16,000 books that the former German dictator and all-around Worst Person in the World collected and, apparently, actually read (most books evidenced Der Furher's propensity to underline passages in pencil, only occasionally doodling butterflies and birds in the margins). Amongst Hitler's Top Books to Take to a Desert Bunker were the collected works of Shakespeare, Robinson Crusoe, Don Quixote, and Uncle Tom's Cabin. Obviously, these books were loved, as they were selected by Hitler for preservation in a Berchtesgaden salt mine. That, or the official in charge of the books' caretaking mistook them for pickling cucumbers. Ryback does not describe how the books were cleaned by their current owner, the rare book collection of the Library of Congress.
Tuesday, Aug 30th
Discussion leader: Sarah Jane Tomkins Book: Middlesex by Jeffrey Eugenides Treat to eat: Bryan brought a fresh veggie platter with homemade hummus and baba ganoush dips Discussion: Sarah Jane started the conversation by praising the wide scope yet human focus of this pseudo-memoir. Gus thought the metaphors were a little obvious, with the personal changes standing in for what was going on in America as a whole. Kim said she got "most of the way through" -- again -- though she did get far enough to complain about the "Asian girlfriend" character. Seriously, this is like the fourth book she hasn't bother to finish this year. Hog admitted he was uncomfortable with all the clinical sex stuff, though he wondered if that was the point. Adolf was quiet, being new to the group. When we got him to open up, he said this book, "if true", showed the decay of the American-er (something like that) way of life, and that the scenes of bootlegging across national borders by the frozen waterways of Michigan gave him some inspiration, though he wondered how much armored weight the ice would hold.
Thursday, Sep 8th
Discussion leader: Augustus Theoharis Book: One Hundred Years of Solitude by Gabriel García Márquez Treat to eat: Sarah Jane's famous ambrosia Discussion: Gus praised the genre of magical realism and gave a long talk about it, forgetting we'd read Borges and Ruolfo six and nine months ago, respectively. Sarah Jane said this was her fourth time re-reading it, and that she saw something new each time. Kim said she hadn't seen ice or snow until she was 14, so the opening always threw her as too matter-of-fact. Hog shared with us some of the other regional authors he thought we might like, and made us laugh when he recounted the racy plot of "Dona Flor and her Two Husbands". It seems like Adolf is still hanging back, but when prodded, he said that the lyrical language reminded him of an unfinished and unpublished novel he had by a friend of his named something like Gertie (sp?), though "obviously" translated poorly. He did say that South America did seem like it could be a nice place to retire to. This led to Sarah Jane showing us all her photos from her last cruise.
Tuesday, Sep 20th
Discussion leader: Hogarth Smith Book: Packing for Mars by Mary Roach Treat to eat: Augustus brought a Godfather's pizza -- he said it was an ironic political statement, but the group consensus was that he was being cheap Discussion: Hog apparently is a big fan of Ms. Roach's books, though some of us shied away at wanting to read a book about dead bodies. He said this wasn't the strongest of her works, but he'd picked up Adolf's interest in rockets. Adolf did seem to appreciate that. But we broke pretty early; the conversation was about Gus being cheap, and this got pretty heated.
Thursday, Oct 6th
Discussion leader: Adolf Hitler Book: A Million Little Pieces by James Frey Treat to eat: Hogarth's Homemade Hoagies. And beer. Discussion: Adolf didn't get a chance to introduce the book and start the conversation, as we all began with talking about how it was a fake. This shocked poor Adolf, who hadn't heard, and had taken the story apparently really, really to heart. He startled us all by screaming that it couldn't be a fake, not at all! He was so adamant, and finally started to break down in tears, crying that the story spoke to him deeply, and he felt it was really the tale of his life. We spent the rest of the evening taking him out for smoothies (which he really likes) and listening to his own stories -- apparently he had quite an unhappy childhood. We were trying to be supportive, but I don't think most of him got all the details (Adolf's accent can get really thick when he's upset). We all gave him hugs, Gus dropped him off at his apartment, and we haven't met since.
The Failure of Analogy in Policy: Debt Edition
Though I'm late to the party on noting Paul Krugman's unpacking of the actual U.S. national debt issue and his smacking down of hysteria over it, I do want to add that this is yet another failure point for analogy and metaphor in policy and politics. Krugman notes that the analogy most often used in discussion of national debt is that the country is like a family, the national economy is like a family's budget -- more specifically, the U.S. debt is often explained as a too-large mortgage that this family has taken out, and now must be repaid. And in general, there are broad strokes and similarities, and indeed analogies can at times offer us ways to wrap our heads around unfamiliar concepts: a peloton of cyclists sometimes moves and reacts like a flock of birds or a school of fish, as the small signals of individual movements propagate and translate into smooth movements of the whole. But, as Krugman shows, just because both involve borrowing money doesn't mean the implications of and appropriate actions for one translate to the other.
Basically, the problem is that analogies (and metaphors) aren't predictive: the peloton may act like a school of fish, but that doesn't mean some of the cyclists should be netted and would be tasty grilled with a bit of lemon. (No, really, the meat would be too tough.)
The same goes for so much of business journalism. One company may be like another, true, but that doesn't mean one is the other, and one's future will not be the other's. At this point, no one would honestly say that Facebook is MySpace and the same will happen to both (though both may end up on the ash heap of history) -- but they did.
The same goes for economics. As Krugman demonstrates:
First, families have to pay back their debt. Governments don’t — all they need to do is ensure that debt grows more slowly than their tax base. The debt from World War II was never repaid; it just became increasingly irrelevant as the U.S. economy grew, and with it the income subject to taxation.
Second — and this is the point almost nobody seems to get — an over-borrowed family owes money to someone else; U.S. debt is, to a large extent, money we owe to ourselves.
Fact-based reporting FTW! It's not only lazy, but it's promoting Bad Ideas to allow the implications of an analogy to run unchecked. (Here we have to keep in mind something from user experience research, and tailor our design/writing to the impulses of users/readers; in this case, the natural impulse is to extend forward the path one has been put on.)
Granted, I've been guilty of employing a metaphor or analogy in a news story, sometimes even to amuse myself in the writing. I hope to keep in mind Krugman's takedown, and always ask, when employing such a rhetorical tool, "but what are the differences, and will they matter more?"
Political News You Can Actually Use
Now this is what I'm talking about. Andy "Don't Call Me Andrew" Sullivan at Reuters actually digs into a candidate's stated policy goals and proposed actions, and looks at what would happen to the U.S. should Paul get elected. It's strange to be so excited at seeing what really should be the job, and Sullivan does have to frame the story within the horse-race format that the other 99% of political news stories use in election years. And all the information Sullivan presents isn't really arcane; it didn't require ProPublica-style investigation, and many of us already knew various pieces of Paul's whacky notions. (Let's leave aside the question of whether voters will and/or should make their choices based on such policy positions or horse-race data, and the chicken-and-egg of whether that's an effect or cause of the 99% horse-race coverage.)
But let's applaud even this collect-and-overview piece. Where are the accompanying reviews of the stated policy plans for all the other candidates? I bet each and every one has at least one "can you believe this?" stated position.
Lab vs. Lab: CSI Edition
“I just met with the conference of Louisiana judges, and, when I asked if ‘CSI’ had influenced their juries, every one of them raised their hands,” Carol Henderson, the director of the National Clearinghouse for Science, Technology and the Law, at Stetson University, in Florida, told me. “People are riveted by the idea that science can solve crimes.” -- from "The CSI Effect" by Jeffry Toobin in The New Yorker. Today's edition presents actual content, not just photos. Linked from each photo is some insight not only into how movie/TV labs look different from actual labs, but what effects on public perception these portrayals have on what a lab can do and mean.
An actual lab:
Lisa Faber, the supervisor of the N.Y.P.D. crime lab’s hair-and-fibre unit. Photograph by Gus Powell.
A TV lab:
Note the shiny surfaces, indirect lighting, the prevalence of hair gel, plenty of open space to move and pace and pedeconference, tailored lab coats, and results that take under two weeks."
Bonus content:
From linked article: "Our set decorators and designers work really hard to not only make beautiful sets, but also sets that are real." Note how "real" can oddly be a subset or secondary consideration to "beautiful". Is your lab beautiful?
As always: please send in photos of your own lab!
Lab vs. Lab: Physics Edition
An actual lab: "Carolyn Pearce uses a piece of equipment at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory to study mineral samples from a nuclear reprocessing site. The data collected will be used for a better understanding of nuclear waste. Jessica Brandi Lifland for USA Today."
Movie lab: Hard to criticize this movie. Note the safety goggles (and how they're being ignored), the outdated-for-the-time equipment, and that Mitch is totally obsessed with data readouts.
Racks of equipment, dingy lighting, looks like little is happening yet the students look like their lives hang in the balance. Yep, a lab.
Okay, the toque blanche and the smiles might be deceptive, but still a lab. (I encourage the reader to look up this clip for a pretty good joke, though.)
Lab vs. Lab: Bio Edition, Part 1
Welcome to the inaugural edition of Lab vs. Lab! An actual lab: Scientists work at a lab at the National Shanghai Center for New Drug Safety Evaluation in Zhangjiang Industrial Park in Shanghai. Associated Press photo by Eugene Hoshiko.
Movie lab: Note the indirect lighting (makes it hard to read instrument outputs, but dramatic), the tailored lab wear, equipment placed aside as through the people were more important.
#DigitalWe is Whee
Frankly, I just don't have enough exposure and experience to figure out when something is a workshop, a conference, or a meetup. They are all very cool, in that you get to see great work being done and learn a lot. It's just that the taxonomy is a bit arcane. In any case, I was lucky enough to attend last week's Digital We from the Social Apps Lab at CITRIS at UC Berkeley. There were fantastic presentations from a range of people within and across disciplines, all with a common interest in increasing people's participation in social causes and society. The participants ranged from a social scientist trying to come up with a "phylogeny of forms" of participation (I'll steal Alenda Chang's links to Kelty's works: “Birds of the Internet” and Two Bits: The Cultural Significance of Free Software) to undergraduates implementing a very Crowdmap-like tool for tracking and combating the spread of dengue fever (sorry, no direct link, but background here).
(You can see more updates by searching the Twitter hashtag #DigitalWe.)
Two notes -- one personal and one professional.
The professional is that one of the overarching themes of the day, sometimes stated explicitly, is that neither technology nor social science would be sufficient to save the day. Not only are both necessary, but both working together (sorry, those who dream of entirely computer-generated products) are needed for designing products, tools, processes that are efficient, effective, and engaging. Hearing this as an I School grad, it was very, very cool to hear that the way we were thinking about things there isn't totally off-base, or limited to our own little world.
The personal is that I would love to work in this sort of environment. Or this environment. So many of the skills we learned at the I School can be and are applied in these projects, though the sharing of expertise, research, and background is still far from transparent and frictionless. Researching how people think of doing things, what their actual problems are, and ways to help them naturally and engagingly make themselves and the world a better place. What can I say? I'm a sucker for the campfire rule.
Future Looking Back (with a Bit of Disgust)
Recent historical novels getting top reviews are making me wonder: what do you think the next few centuries will look back and see as our daily barbarisms? War and racism, of course, but I'm asking more about how we look back to when a small cut on a finger could lead to death, or when people thought regular bathing was unhygienic. What do we do now? Use a device to connect to the internet? Eat in front of other people? Chemo? Shampoo and conditioner?
Buffalo Bill's Defunct
The other day on NPR's Talk of the Nation, a caller had to admit that an on-air guest had stolen his thunder; the guest had just said that the current Presidential race is more like a reality show than a campaign. But even the guest wasn't being entirely original. Jezebel was on it and noted TPM noting it, showing even Republican candidates (current and former) placing themselves in this narrative of narrativity. But those were just the explicit castings, and not the real problem -- news relies on narrative, after all. The real problem is that even the "good" news outlets have long implicitly and explicitly favored narrative drive over any other content. That "reality show" is overwriting "horse race" doesn't make "horse race" any better for our future.
Though my love for NPR can perhaps verge into the stalker-y, it frustrates me to no end that the Political Junkie and other coverage is perpetually stuck on who's up and who's down in polls, perception, points. And it's not just NPR: the horse race is the standard template for talking about politics no matter you choose as your most trusted name in news. There have been the odd chart on who would benefit and who would suffer if 9-9-9 somehow became the law of the land, but that's the exception. (And this bit of policy analysis was, ironically, enabled by the same excessive and unworkable oversimplifications of the plan; who's been digging into what tax burdens for the poor would look like under a Romney or Huntsman plan? Actually, not radically different in shape, just in scale.)
Ed over at Gin and Tacos implies that the desire for narrative might even be shaping the race, rather than the race shaping the narrative. The networks are so hungry to be able to present the conflict of a nail-biter, Ed says, might be what ballooned one poll results into a perception that Gingrich could actually be a viable candidate. Well, there has to be some other reason, right? It's not like Gingrich is a viable candidate.
Even the excellent Pew Research Center's Project for Excellence in Journalism ends up with this as the foundation for their analyses. If you look at their recent study of how news media and blogs have treated the candidates, you can tease out that the rise or fall in how a candidate is covered is fueled by talk about their standings in the polls. The horse race is the CDO or CDS market driving the Dow and, like that bad situation, we're ignoring how solid or crappy the underlying mortgages (policies) are.
So the video introductions to the Republican debates on CNN, MSNBC, Fox, and others look like nothing so much as the opening titles for any random season of "The Apprentice". What were they before? Perhaps more like an into to a title fight, with who's favored and who's the underdog. Seriously, that's hurting America, either way. At least, as some Americans seems to seriously desire a motivational speaker as their President, we're just being more honest about making it entertaining.
Campagnolo, Logos, and the Jet Age
Christian Annyas is, apparently, a bike as well as typographic geek. On his blog he takes a look at jersey design and component logos in the most recent Tour de France. How did Christian know how to entice me with two of my favorite things? I will admit to being a bit confused by his judging that this year's jerseys are "possibly the best designed of all time." This is in part because he savages most of the designs while the few he lauds... well, I just don't see Leopard-Trek as particularly good layout and color. Granted, there are none of the truly weird designs of the past such as the Carrera bib shorts or the not-so-slimming-stripes of Atala (one year they were helical like a barber's pole), but the class of 2011 seem to diverge between carelessly gaudy (Saur-Sojasun, I'm looking at you) and plain (Team Radioshack and, again, Leopard-Trek). Team Sky does manage to pull off the understated, in part because of the black base but also, I think, due to the higher placement of the green band; this means the black flows over the breastbone-to-belly area, which is problematic when most people are in a proper cycling position. In contrast, the Leopard-Trek jersey just looks like it gave up at some point and lacks balance. I agree with Annyas on AG2R La Mondiale, BMC, and Garmin, but three good design solutions out of 22, with a few in-betweeners -- would your company take that as a win?
But what I want to get to specifically is the Campagnolo logo, as it changed between 1960 and 1974. I'd love to Christian to address this (and the other logos), because I'm sure he could add comments that would be a hundredfold more historically and typographically insightful. I'd also love to hear from any people with experience in this area.
Let's look at the 1960 version:
 The image Christian found looks to be a slightly decayed sample, or scanned off of a porous surface such as a cardboard component box; an older but cleaner version can be seen on the Velo-Retro site (it's to Christian's credit that Google searches for "Campagnolo 1960" returns his site pretty high up in the results). So we can see that the radiant lines around the globe and the letter shadows aren't meant to look distressed by design (though that may have been how most people saw it on shirts, boxes, paper, given the print technology of the day). But the logo does look to be of a time: I look at it and see a newspaper masthead or a movie studio sign from a day when men wore hats and women wore gloves. The globe signifies "worldwide", but at that time travel was hard, the world as a whole wasn't accessible, and so the idea of seeing the globe as a whole was new, like a rising sun.
The image Christian found looks to be a slightly decayed sample, or scanned off of a porous surface such as a cardboard component box; an older but cleaner version can be seen on the Velo-Retro site (it's to Christian's credit that Google searches for "Campagnolo 1960" returns his site pretty high up in the results). So we can see that the radiant lines around the globe and the letter shadows aren't meant to look distressed by design (though that may have been how most people saw it on shirts, boxes, paper, given the print technology of the day). But the logo does look to be of a time: I look at it and see a newspaper masthead or a movie studio sign from a day when men wore hats and women wore gloves. The globe signifies "worldwide", but at that time travel was hard, the world as a whole wasn't accessible, and so the idea of seeing the globe as a whole was new, like a rising sun.
The revamp Christian next shows has a vastly simplified globe (still with latitude and longitude lines), fewer rays, and no drop shadow to the lettering.
 I don't really feel qualified to comment on the font change -- there's a slight modification of stroke width, letter height, and something new with the "g" -- but the overall sense is one of lifting off from layers of cruft, of more abstraction from the earth, which is by 1974 something everyone has seen from satellite photos. What else has happened? Two words: Pan Am.
I don't really feel qualified to comment on the font change -- there's a slight modification of stroke width, letter height, and something new with the "g" -- but the overall sense is one of lifting off from layers of cruft, of more abstraction from the earth, which is by 1974 something everyone has seen from satellite photos. What else has happened? Two words: Pan Am.
In 1957, Pan Am moved from a "globe and wing" logo to the modern version (some images and unverified background). You can see a possible influence on Campagnolo's later change in the stripping of real features from the globe, the recognition of recognition of the planet as an icon. Pan Am's influence around the Western world was deep and wide: its modern HQ broke the Manhattan skyline in 1963, and even before Apollo 11 Pan Am was seen as the logical way to get into space (note: the historical "Clipper" or Orion Space Plane is currently in collection at the Sci-Fi Airshow).

 Of course, chronology does not mean copying. The point I mean to make is that it could be that similar influences and perceptions led Campagnolo towards a certain direction. Years passed between Pan Am's major redesign effort (which included years of research) and Campagnolo's simplification. In fact, I'm asking all of you who know more about design work from that period to chime in.
Of course, chronology does not mean copying. The point I mean to make is that it could be that similar influences and perceptions led Campagnolo towards a certain direction. Years passed between Pan Am's major redesign effort (which included years of research) and Campagnolo's simplification. In fact, I'm asking all of you who know more about design work from that period to chime in.
And this isn't to say Campagnolo was full speed ahead to the Space Age and modernist design. These two designs for frame stickers are dated by Velo-Retro as coming from 1953 and 1967. Both seem to use the pre-1970-redesign font, though the latter seems to have done away with the longitude lines, probably due to the small size of the sticker, which was to go onto one or more of the tubes of a bike frame. Both have the World Championship "rainbow" colors across the globe, though.
And how did Campagnolo move into the future past the Space Age, post 1970s? By simply abstracting out the globe entirely. The brand isn't just worldwide, it is the world.